Cholelithiasis, or as it is usually called more popularly, “stones in the gall,” refers to the formation of gallstones, i.e., crystalline sediments, inside the gallbladder. The presence of gallstones can be accompanied by obvious symptoms, such as vomiting, acute abdominal pain, indigestion, etc., but there are also cases where it does not give obvious clinical signs, which makes it difficult to recognize the problem early. However, thanks to laparoscopic cholecystectomy, the surgical removal of the gallbladder now has a significantly reduced recovery time and almost zero risk of postoperative postoperative complications, thus facilitating the immediate return of patients to their daily lives.
The gall bladder
The gallbladder (commonly known as bile) is a pear-shaped organ located under the right side of the liver.
The main function of the gallbladder is to collect some of the digestive fluid – or otherwise, bile – produced by the liver.
The gallbladder releases this fluid immediately after eating when needed to aid in the digestion of primarily fatty substances. Bile travels through narrow tubular channels into the small intestine.
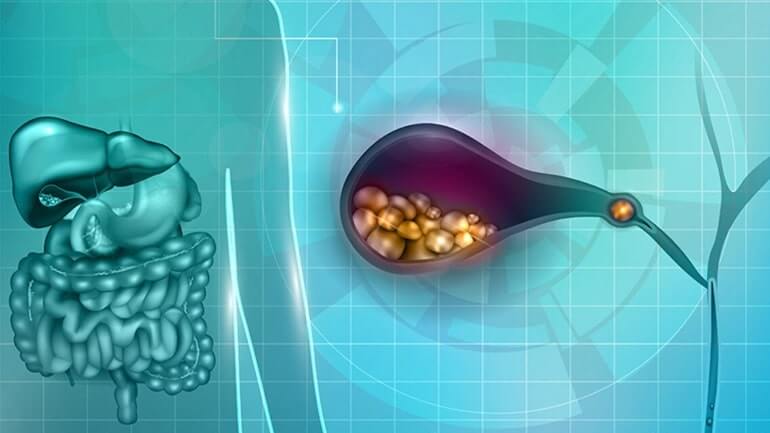
Cholelithiasis
Gallbladder problems are usually caused by the presence of gallstones (stones).
These salts are mainly formed from cholesterol and bile salts in the gallbladder or bile duct. The causes that create gallstones are not known, so there are no ways to prevent their formation. If these stones move into the cystic duct, they block the flow of bile to the intestine and cause the cyst to swell, resulting in acute abdominal pain, vomiting, indigestion, and, in some cases, fever. In addition, if the gallstone blocks the common bile duct, then jaundice (yellowing of the skin) or pancreatitis may occur.
Having gallstones can be accompanied by symptoms (vomiting, indigestion, acute abdominal pain, heartburn, etc.), but many times they are asymptomatic. The safest, most painless, and economical method of diagnosis is ultrasound.
The most appropriate and safest treatment for cholecystitis is surgical removal of the gallbladder, which does not cause any digestive disturbances in most patients.
In the past, the removal of the gallbladder meant a large incision, a stay in the hospital for several days, and postoperative pain. In the 1990s, things changed, and fortunately, the surgery to remove the gallbladder has been done laparoscopically since 1989.
laparoscopic cholecystectomy
With the appearance of the revolutionary method of laparoscopy in the early 90s, the facts of cholecystectomy changed. In this method, a laparoscope is inserted through a tube
5 to 10 millimeters in diameter, which allows the surgeon to see the patient’s internal organs at a magnification of 10 to 15 times.
At the same time, other tubes with a diameter of 3-5 millimeters are inserted into the abdomen, allowing the surgeon to work inside. From the same incisions, intraoperative cholangiography or bile duct research (colonoscopy) can be performed if required.
However, in less than 1% of patients (when it comes to a specialized surgical team) this method cannot be applied, due to special conditions. The decision to have an “open” operation is at the discretion of the surgeon before or even during the operation.
Advantages of laparoscopic cholecystectomy over open surgery
- Minimal surgical trauma (one 1 cm incision and three 0,5 cm incisions)
- Quick recovery
- Minimal blood loss
- Quick discharge from the hospital
- Lower cost of hospitalization
- Quick return to work and daily activities
- 10-15x image magnification and better lighting
- Minimize postoperative postoperative pain.
- Virtually eliminate trauma-related postoperative postoperative complications (perfusion, dehiscence, hernia, chronic pain, etc.)
- Fewer respiratory and cardiovascular complications
- Reduction of the possibility of creating postoperative postoperative adhesions and cardiovascular complications
- Ability to treat patients in serious conditions such as heart surgery patients, overweight patients, or patients in the ICU.
- Also, in laparoscopic cholecystectomy, complications are extremely rare, and patients return to their normal activities very soon. They are discharged the day after surgery.
For detailed information and any questions, please contact Efstathios Bathrellos at 6936606664 or Therapis General Hospital at 210 7291111.
Book your appointment today at 210 729 1111 or by filling out the form you will find HERE.
Find Therapis General Hospital on social media:
Instagram | Facebook | LinkedIn