What is sunburn?
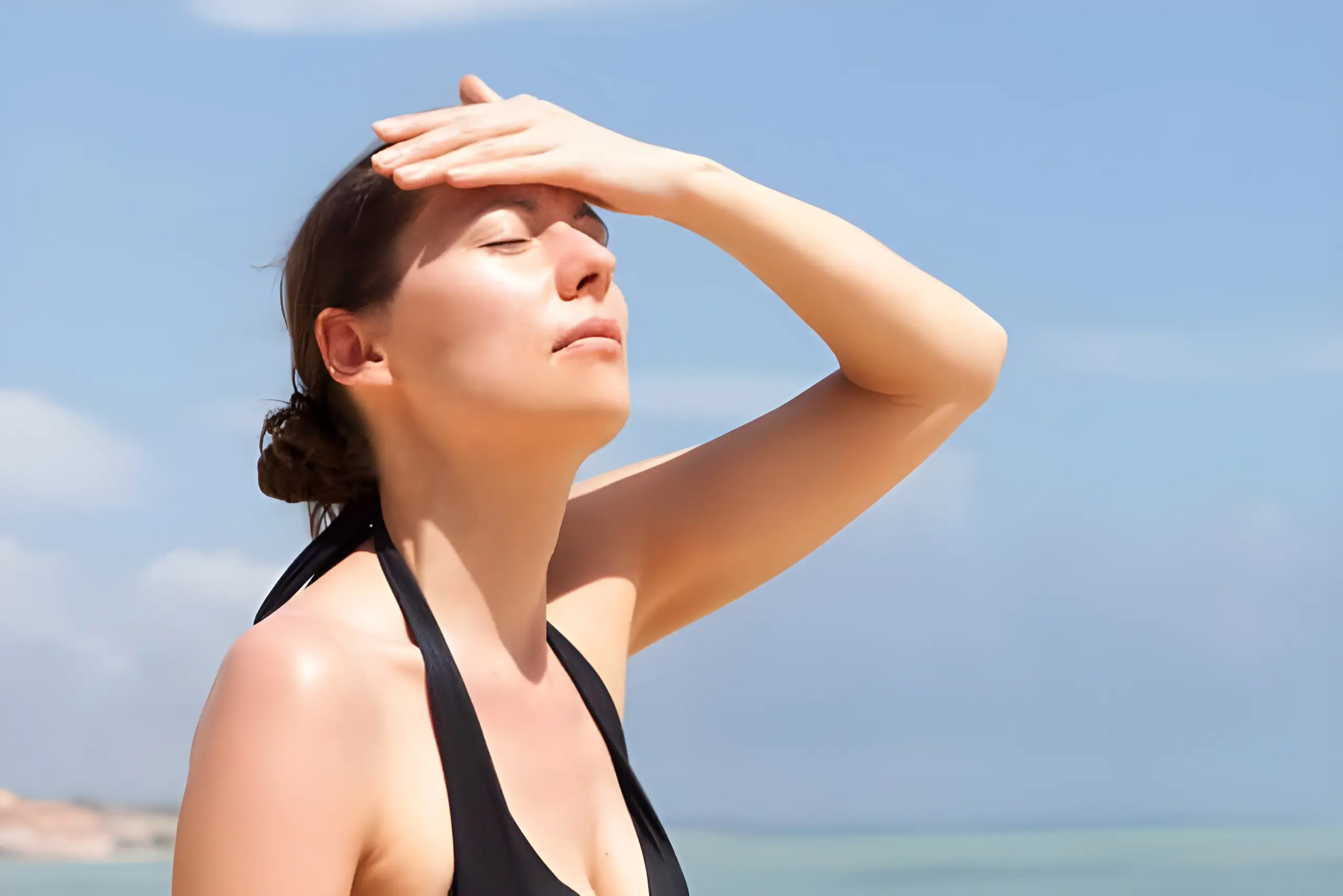
Imagine yourself enjoying the summer sun while doing your favorite sport. Suddenly, you start to feel a slight headache, but you don’t pay much attention to it. As time passes, the headache becomes more intense and you begin to feel dizzy and nauseous. If you have ever experienced these symptoms, chances are you have suffered from a form of heatstroke commonly known as sunstroke.
Sunstroke is the most common type of heatstroke, resulting from prolonged exposure to the sun’s thermal radiation, often leading to heat exhaustion. This condition occurs particularly due to prolonged exposure of the head and neck to the sun’s ultraviolet rays during the hot summer months.
How is the temperature of the human body regulated?
Normally, humans and mammals have thermoregulatory mechanisms in the brain to maintain a stable internal temperature (approximately 36.8 ± 0.4°C in humans). Special nerve cells, known as thermoreceptors, detect changes in the ambient temperature and signal the brain to increase the temperature. The brain’s temperature regulation center then sends messages to the sweat glands and blood vessels on the skin’s surface, leading to sweat secretion and vasodilation, respectively. This combination of reactions helps maintain our body temperature.
Causes of sunburn
Sunburn can be caused by various factors, such as exposure to hot environments or high temperatures, wearing warm clothing that prevents sweat evaporation and body cooling, alcohol consumption (which affects temperature regulation), and dehydration due to increased sweating.
Symptoms of sunburn
The symptoms of sunstroke can vary depending on its severity:
Mild form:
Dizziness
Fatigue
Redness of the skin
Sweating problems
Ringing in the ears
Moderate form:
Headache
Nausea
Vomiting
Rapid breathing
Tendency to faint
Muscle weakness or cramps
Reduced sweating
Burns or blisters on the skin
Severe form:
Delirium and confusion
Convulsions
Hallucinations
Dark urine (sign of dehydration)
Pale skin
Duration of sunburn
If the symptoms of sunburn do not improve within an hour, it is recommended that you seek medical attention. Depending on the severity of the sunburn, it can last up to 2 days, but the body usually needs about 2 months to 1 year to fully recover from the effects of sunburn.
It is vital to recognize the symptoms of heatstroke and seek immediate medical attention to avoid serious complications.
Prevention of sunburn
- Limit sun exposure: especially between 11:00 a.m. and 5:00 p.m., when the sun’s rays are strongest.
- Protect yourself: Wear a hat and sunglasses and apply sunscreen with a high sun protection factor (SPF) when outdoors.
- Choose comfortable clothing: Opt for light, loose-fitting clothing that allows your body to regulate its temperature effectively.
- Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of fluids to stay hydrated, promoting proper sweating and maintaining normal body temperature.
- Avoid alcohol: Avoid drinking alcohol, as it can affect your body’s ability to regulate its temperature effectively.
- Choose light meals: Eat light, nutritious meals rich in fruits and vegetables to support your overall well-being.
What is heatstroke?
Heatstroke is a serious condition characterized by overheating (hyperthermia) of the body and requires immediate medical attention. It can be classified into two clinical forms: classic heatstroke and exercise-induced heatstroke.
Classic heatstroke: It is mainly caused by exposure to extremely high temperatures.
It is more common in people with inadequate thermoregulatory mechanisms, such as the elderly or people with cardiovascular problems.
Symptoms of heatstroke
- High body temperature: Increased body temperature is a primary sign of heatstroke.
- Mental disorders: Confusion, seizures (especially in children), delirium, irritability, and coma.
- Changes in sweating: The skin becomes hot and dry, with reduced or absent sweating (a late symptom).
- Nausea: Feeling sick or needing to vomit.
- Headache: Severe headache, often located in the forehead or throughout the skull.
- Change in skin color: The skin becomes red as the body heats up.
- Breathing: Breathing may become faster and shallower.
- Heart rate: The heart is under increased pressure as the body tries to cool down, causing an increased heart rate.
It is vital to recognize the symptoms of heatstroke and seek immediate medical attention to avoid serious complications.